


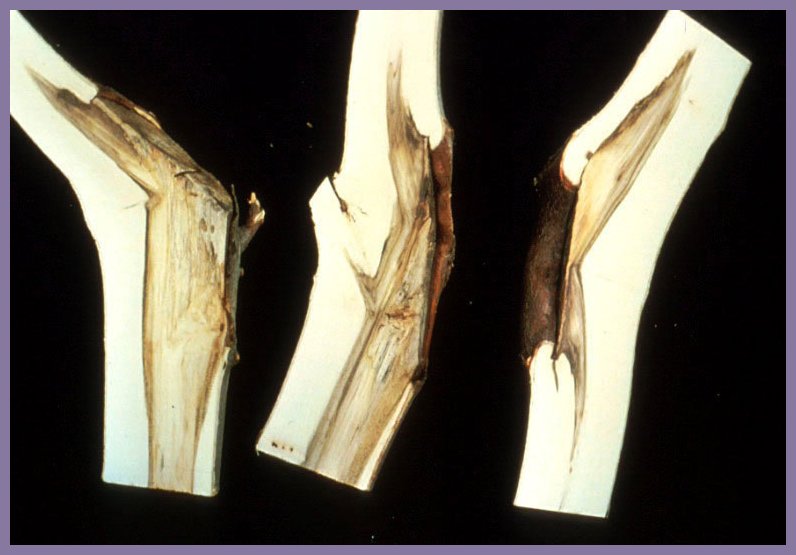
Good and Flush Cut on Oak

Flush cut thus resulting in a canker. Honey Locust.
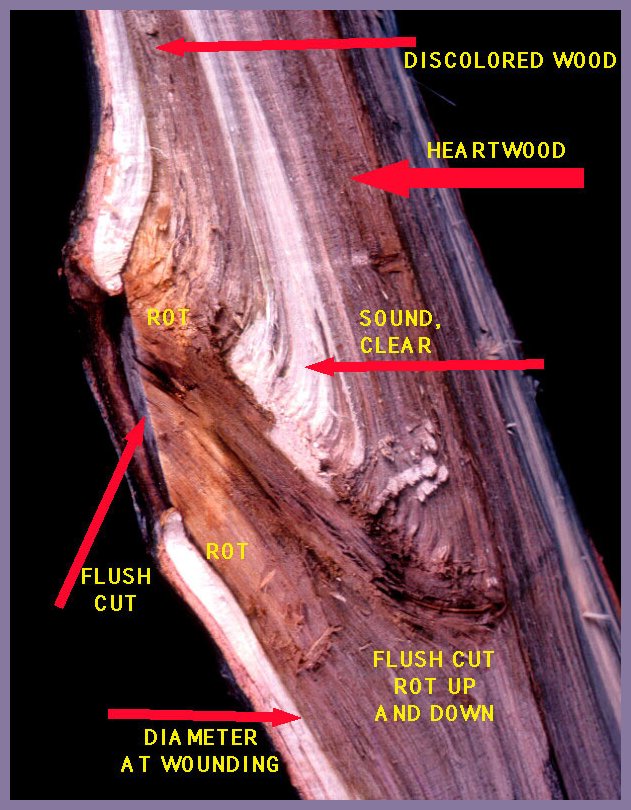
Black Walnut
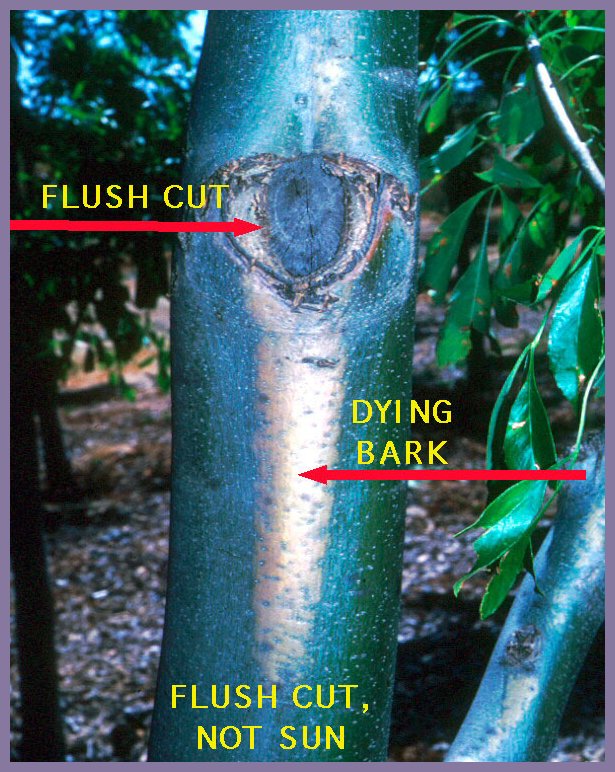

Flush Cut in Florida
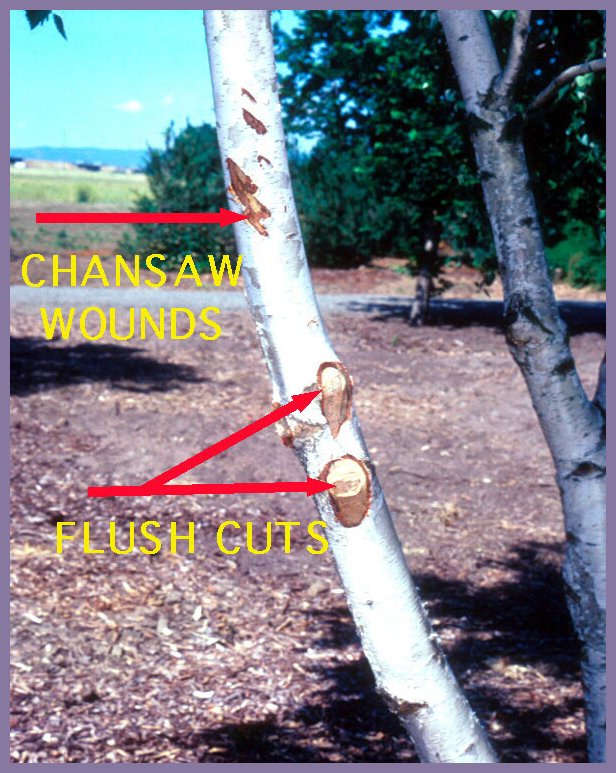

Birch
 Internal
response to flush cuts.
Internal
response to flush cuts.

Boundaries also form at the base of branches as they die. The
boundaries resist the spread of infections into the tree from organisms in the
symplastless branch. Because the symplastless branch is mostly cellulose, which
is made up of glucose - sugar - fungi can use the symplastless branch as a
source of food while they "press" against the boundary within the branch base.
Arrows A show the boundary. When pruning, do not leave stubs as food for fungi,
and do not cut branches flush with the stem - flush cuts - thus removing the
tissues that form the boundary. Do cut as close as possible to the swollen base
or collar of the branch, but do not injure or remove the swollen base or collar.
Arrows B show where the trunk tissues grew around the branch tissues.
(Images from SHIGO, 2002 - Cds)
Dictionary MAIN PAGE
Text & Graphics Copyright © 2004 Keslick & Son Modern Arboriculture
Please report web site problems, comments and words of interest, not
found.
John A. Keslick, Jr.